![]()
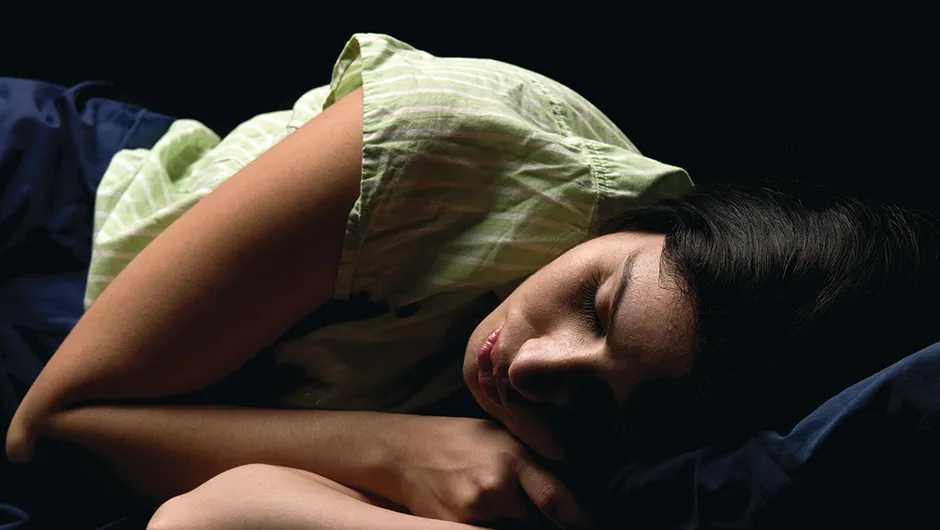
Sleep is a fundamental aspect of human life, playing a critical role in maintaining physical and mental health. During sleep, our bodies repair and rejuvenate themselves, and our brains process and consolidate memories and learning from the day. Adequate sleep is essential for optimal functioning, and chronic sleep deprivation can have severe consequences on our overall health.
The Benefits of Sleep
1. Physical Restoration: Sleep helps to repair and regenerate damaged cells, build bone and muscle, and strengthen the immune system.
2. Cognitive Function: Sleep plays a crucial role in brain function, enhancing cognitive abilities such as attention, memory, and decision-making.
3. Emotional Well-being: Sleep helps to regulate emotions, reducing stress and anxiety, and promoting a sense of well-being.
4. Cardiovascular Health: Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes.
The Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
1. Impaired Cognitive Function: Lack of sleep can affect attention, memory, and decision-making abilities, leading to decreased productivity and increased risk of accidents.
2. Mood Disorders: Sleep deprivation can lead to irritability, anxiety, and depression, affecting overall mental health and well-being.
3. Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes.
4. Weakened Immune System: Sleep plays a crucial role in immune function, and chronic sleep deprivation can weaken the immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses.
Tips for Improving Sleep
1. Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, including weekends.
2. Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment: Make your bedroom a sleep haven by ensuring it is dark, quiet, and cool.
3. Avoid Stimulating Activities Before Bedtime: Avoid stimulating activities like exercise, watching TV, or scrolling through your phone before bedtime.
4. Avoid Caffeine and Nicotine: Both caffeine and nicotine can disrupt sleep patterns and reduce the quality of sleep.
Sleep Disorders and Treatment Options
1. Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep, often treated with cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or sleep medications.
2. Sleep Apnea: Pauses in breathing during sleep, often treated with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy or oral appliances.
3. Restless Leg Syndrome: Uncomfortable sensations in the legs during sleep, often treated with medication or lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Sleep is a vital aspect of overall health, and prioritizing it is essential for maintaining physical and mental well-being. By understanding the benefits of sleep, the consequences of sleep deprivation, and implementing tips for improving sleep, individuals can take steps towards achieving better sleep and overall health.